The Ultimate Vitamin D Talk
The Ultimate Vitamin D Talk
What is Vitamin D?

Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that is essential for several vital functions in the body. It is primarily known for its role in maintaining strong and healthy bones by aiding in the absorption of calcium and phosphorus.
It is obtained through exposure to sunlight, certain foods like fatty fish and fortified products, and supplements.
Deficiency in vitamin D can lead to bone-related problems like rickets and osteoporosis, impair immune function, and potentially impact mood, making it crucial to maintain adequate levels of this vitamin.
The video that this article references breaks down a few different studies that all relate to vitamin D and it's critical role in the human body. All of these studies aim to prove and demonstrate the important of obtaining and maintaining healthy levels of vitamin D.
Clinical Research Study #1
Study Name: Pre-infection 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 levels and association with severity of COVID-19 illness
Study Reference: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0263069
Study Conducted: Study came out of Israel February 3rd 2022
Researchers looked at whether having low levels of vitamin D before getting COVID-19 makes people sicker or more likely to die from the virus.
The study looked at the medical records of people who were admitted to the Galilee Medical Center in Israel between April 7th, 2020 and February 4th, 2021, and tested positive for COVID-19. They checked if these individuals had their vitamin D levels measured 14 to 730 days before testing positive.
The study was extremely well executed and very well corrected for
- prior medical histories
- age
- used previous vitamin D readings
Results
In the graph to the right, the boxes represent the range of vitamin D values within the middle 50% of cases (interquartile range). The lines extending outside the boxes indicate the highest and lowest values within 1.5 times the interquartile range.
Any values that fall beyond these lines are considered outliers and are represented by empty circles.
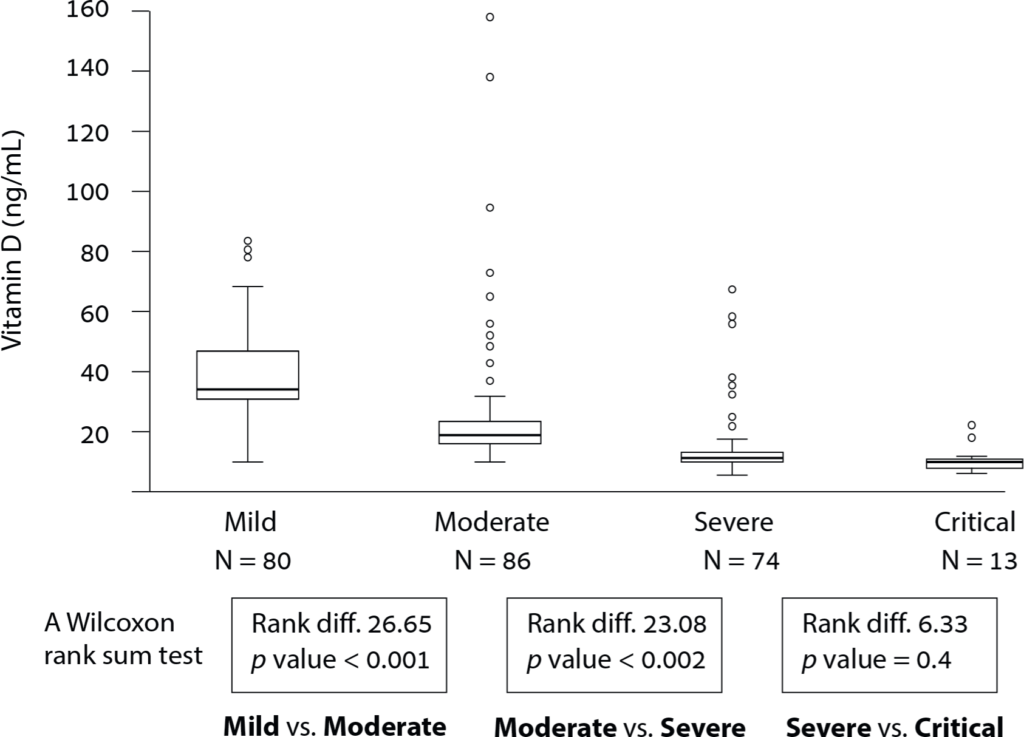
The people who suffered most (Critical N = 13) had the lowest vitamin D levels. Conversely, people that had reasonable levels of vitamin D were in the Mild (N = 80) category (regardless of age, regardless of history).
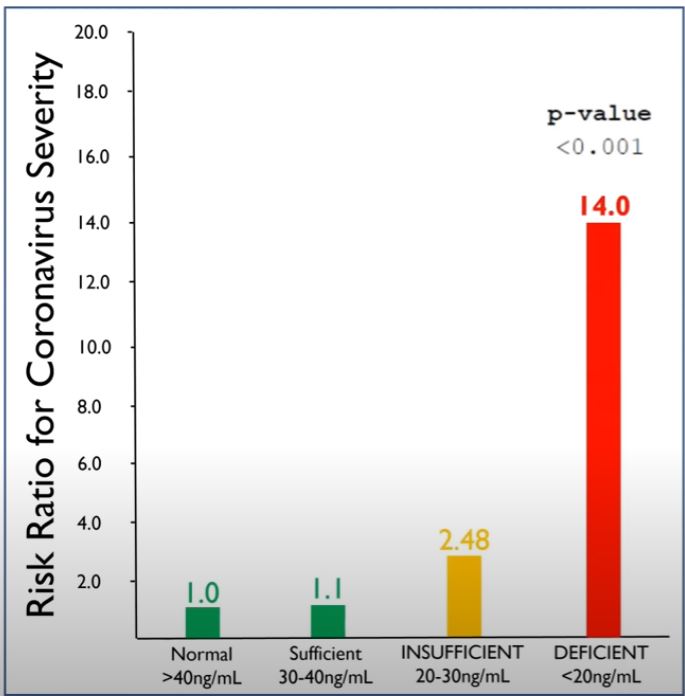
This chart illustrates the risk ratio correlation between the severity of symptoms that are experienced with COVID and the levels of vitamin D in the body.
There is a 14x risk factor increase in the severity of COVID symptoms for participants that were deficient in vitamin D. Conversely there is no increase in risk for normal levels of vitamin D.
What does this study tell us? Having higher amounts of vitamin D in the body reduces the severity of COVID 19 symptoms.
It is recommended that you're in the 40+ng/mL (Nanogram units per milliliter) of vitamin D per day.
Clinical Research Study #2
Study Conducted: Published 9th April 2020
This study looked at the levels of vitamin D in COVID-19 patients and how it affects their health. They studied 212 patients with confirmed COVID-19 from different hospitals.
They found that most patients had mild symptoms. The average vitamin D level was 23.8 ng/ml. Critical cases had the lowest vitamin D levels, while mild cases had the highest. Vitamin D levels were linked to how sick people got. Most patients didn't have enough vitamin D, but they were less likely to have severe symptoms.
The study showed that higher vitamin D levels were linked to better outcomes. For every increase in vitamin D levels, the odds of having mild symptoms instead of severe symptoms went up by about 8 times. Surprisingly, the odds of having mild symptoms instead of critical symptoms went up by about 20 times.
Interesting point: The study did account for multiple corrections (e.g. Correcting for age and prior history etc...) but it didn't really change the result.
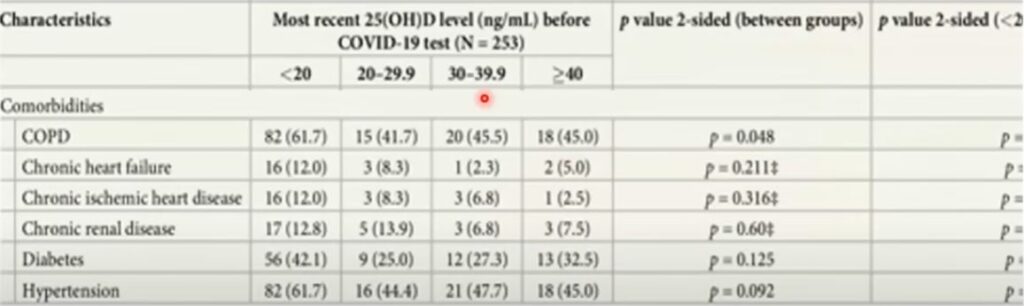
Interesting point 2: The people that scored high on their Vitamin D levels (i.e. > 40 ng/mL) still had comorbidities associated with them. For example, 45% of the participants that scored highly had hypertension and nearly a 1/3 had diabetes.
The only thing that distinguished them between mild vs severe COVID symptoms were their vitamin D levels. You can see the power of having a maintaining a high level of Vitamin D in your body.
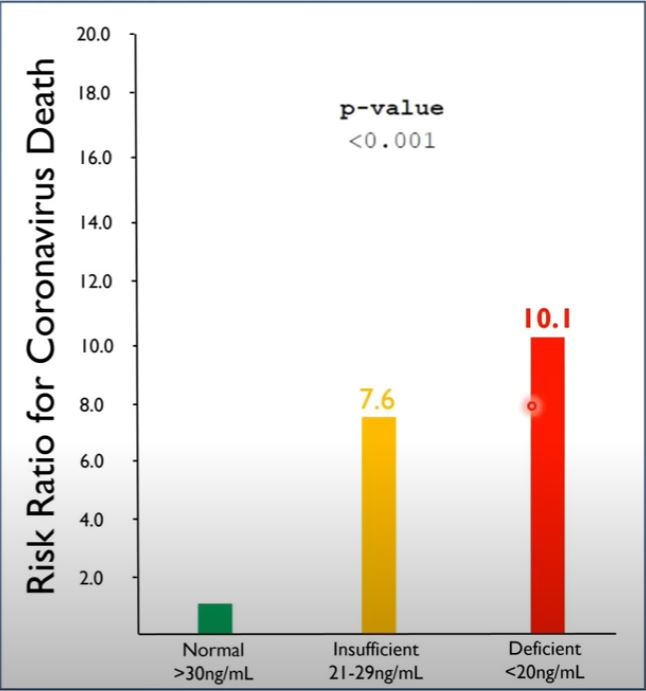
You can see in the diagram to the left the risk multiplier for participants that were deemed to have insufficient or deficient levels of vitamin D.
This chart is very similar to the first study referenced and reaffirms the benefit of having high vitamin D levels.
What does this study tell us? Having higher amounts of vitamin D in the body reduces the severity of COVID 19 symptoms.
Clinical Research Study #3 - Maasai Tribe and the Correlation

The median Vitamin D level for the Maasai males in this study was 42ng/mL. Remember, we are aiming for anything over 40 as healthy.
Having a level >40 ng/mL allows the bodily process that creates Vitamin D to self-correct and a feedback loop begins.
We also know ancestrally, men in the 40ng/mL and women in the 50 ng/mL is considered "normal" for the healthy indigenous populations.
Clinical Research Study #4
Study Name: Demographic Differences and Trends of Vitamin D Insufficiency in the US Population, 1988–2004
Study Conducted: 1988-2004
This study aimed to assess trends in vitamin D insufficiency in the US population. Researchers compared data from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III) conducted between 1988 and 1994 with NHANES data collected from 2001 to 2004. They analyzed serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) levels in a total of 18,883 participants from NHANES III and 13,369 participants from NHANES 2001–2004.
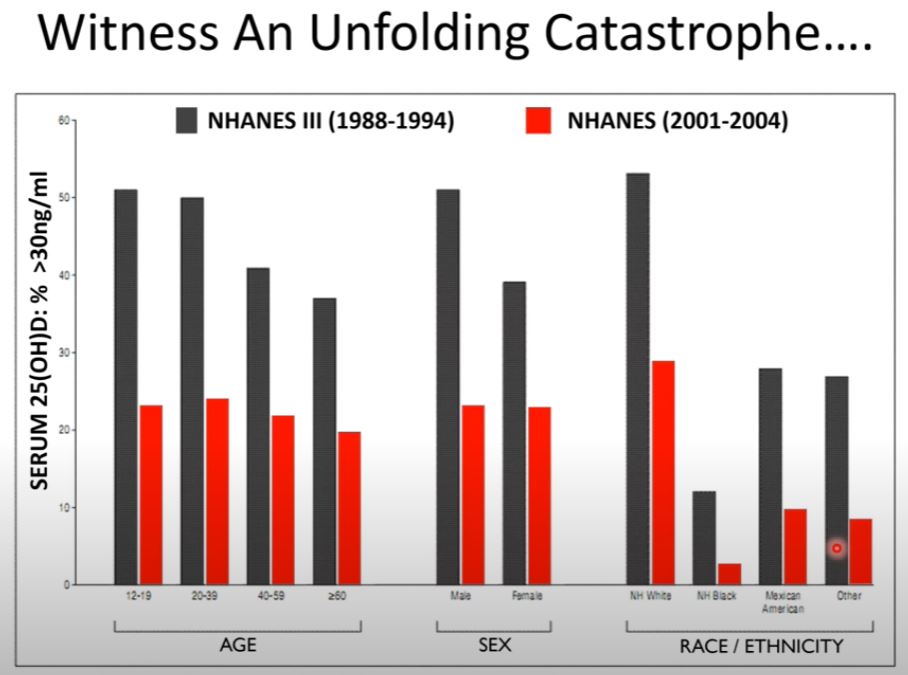
As you can see, levels of Vitamin D have dramatically reduced in all metrics and are below the healthy level.
Clinical Research Study #4
Study Name: Vitamin D and the scientific calcium dogma: understanding the 'Panacea' of the sun
Study Reference: European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2012) doi:10.1038/ejen.2012.78

Almost a century ago, scientists came up with the idea that vitamin D mainly controls calcium levels in the body. This idea is still widely accepted today, even though there's evidence challenging it.
If we take a step back and look at it from a simple, non-scientific perspective, it's a bit puzzling. Vitamin D, often called the 'sunshine vitamin,' is linked to more than just calcium. Many cultures and health traditions have appreciated the sun for various benefits. So, why did science focus so much on vitamin D's role in calcium regulation and ignore other aspects? It seems that this happened because it was easy to see how vitamin D affected our bones, easy to test for, and experts in the field emphasized it. They didn't pay as much attention to other potential effects of vitamin D, missing the bigger picture."
Human Evolutionary Environment
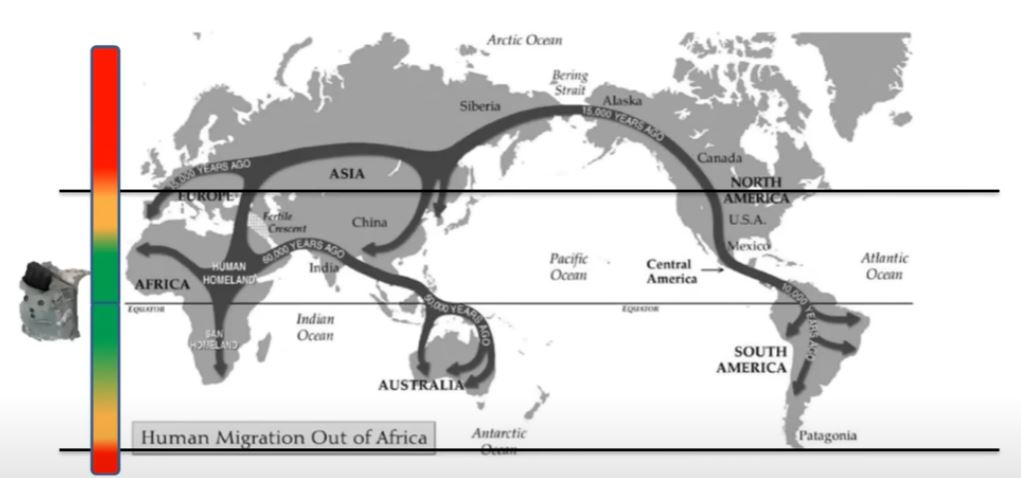
Key Takeaways:
- We originally evolved in an intense UVB environment - part of our design
- Migration over millennia drove commensurate skin pigmentation adaptation
- Tradeoff: Between UV Excess (e.g. Folate), and adequate synthesis of 25(OH)D
Clinical Research Study #5
Our body has natural defenses against certain infections, especially those caused by tiny intruders that can hide inside our cells. One of these defenses involves a molecule called TLR2/1 and vitamin D, which together activate special white blood cells called monocytes. These activated monocytes produce a substance called cathelicidin, which helps fight off intruders like the tuberculosis bacterium.
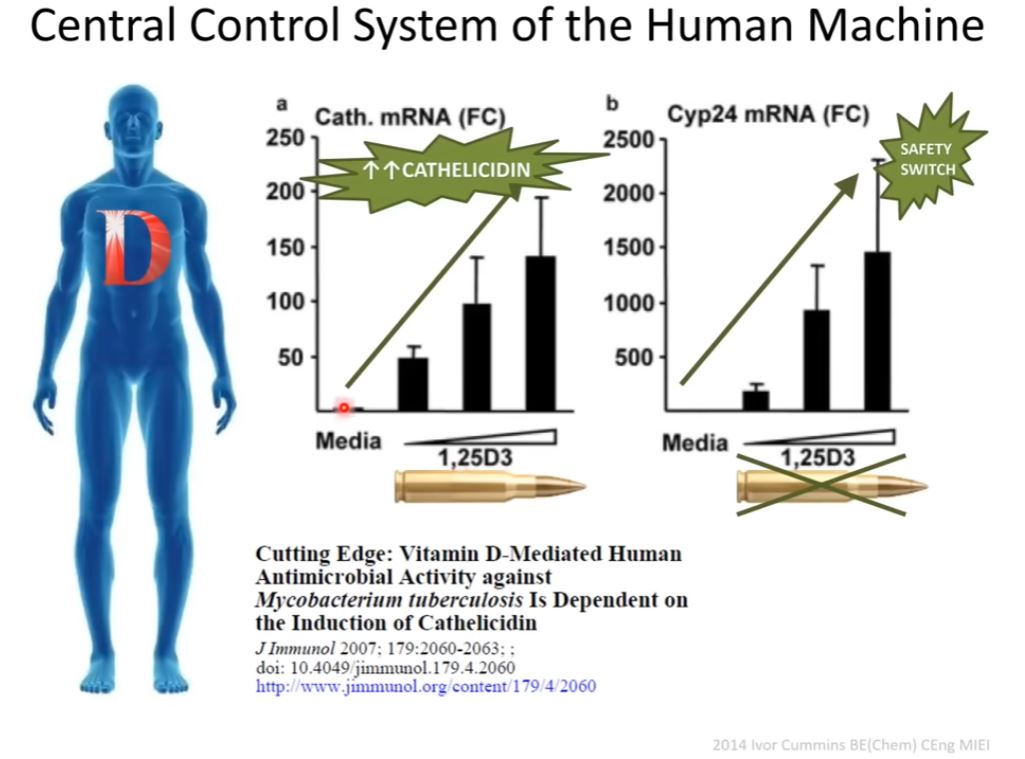
To see if cathelicidin is really necessary for this defense, scientists conducted experiments using cells. They first infected these cells with tuberculosis bacteria and then treated them with a form of vitamin D called 1,25D(3). This vitamin D not only helped the cells fight off the bacteria but also made them produce cathelicidin.
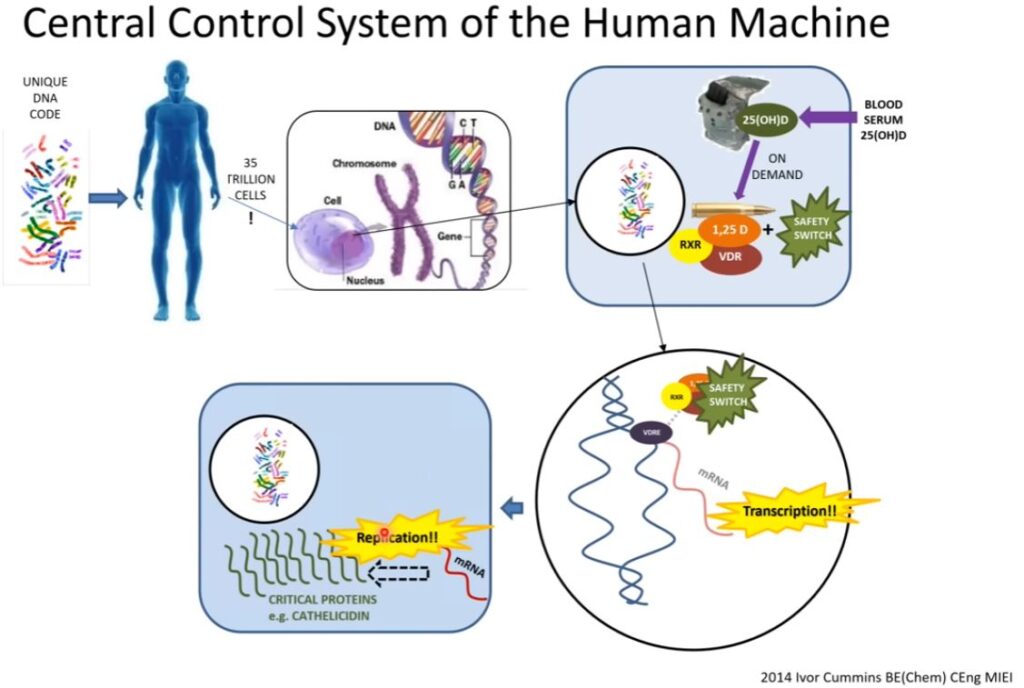
To check if cathelicidin is essential, scientists used a technique called small interfering RNA (siRNA) to block its production in the cells. When cathelicidin was blocked, the cells couldn't fight the bacteria as well, and the bacteria grew more inside the cells.
In simple terms, this research shows that cathelicidin is a crucial part of our body's defense against tuberculosis when vitamin D is involved."
So, How Do We Get High Vitamin D Levels?
1. Consume Nutrient-Dense Foods
Eating a balanced diet rich in vitamin D can help maintain healthy levels. Foods like fatty fish (e.g., salmon, mackerel), fortified dairy products, and eggs are excellent sources of vitamin D.
2. Avoid Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance, a condition linked to diabetes and obesity, can negatively impact vitamin D levels. Maintaining a healthy diet and regular exercise routine can help prevent insulin resistance and improve overall vitamin D status.
3. Reduce Inflammation
Chronic inflammation, often associated with conditions like diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and autoimmune disorders, can deplete vitamin D levels. Managing inflammation through a healthy lifestyle can help maintain adequate vitamin D levels.
4. Get Healthy Sunlight Exposure
Sunlight is one of the most effective ways to boost vitamin D levels. Aim for regular, moderate sun exposure without sunscreen for short periods, especially during midday. However, avoid excessive sun exposure to prevent sunburn and skin damage.
5. Consider Vitamin D Supplements
For those who struggle to get enough vitamin D through diet or sunlight, supplements can be a useful tool to maintain adequate levels. It’s recommended to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dosage based on individual needs.
Summary of Vitamin D
Vitamin D plays a critical role in multiple aspects of health, including immune function, bone health, and infection defense. Numerous studies have demonstrated the importance of maintaining adequate vitamin D levels for preventing severe illness, particularly in the context of COVID-19. Higher vitamin D levels have been consistently associated with better health outcomes, including reduced severity of COVID-19 symptoms, improved cardiovascular health, and enhanced immune function.
As research continues to uncover the far-reaching effects of vitamin D on human health, it is clear that maintaining adequate levels is crucial. Whether through sunlight exposure, diet, or supplementation, prioritizing vitamin D can lead to improved overall health and a reduced risk of chronic diseases.
Daily Crossword
